|
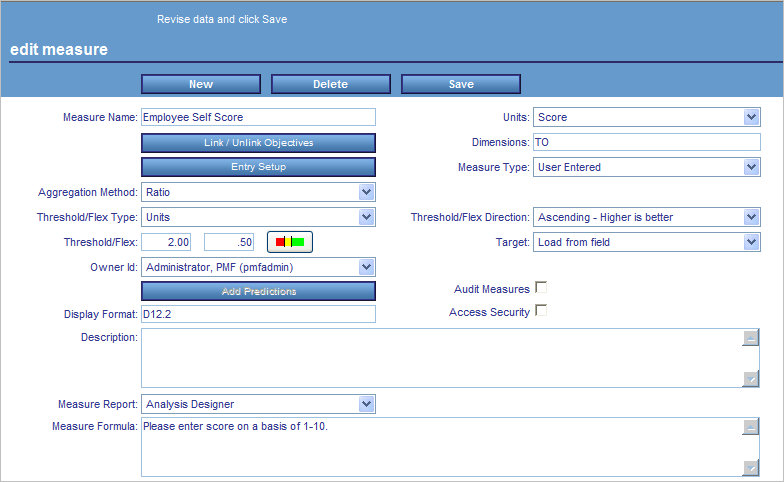
Measure Name
|
The measure you
are editing.
|
|
Units
|
The unit of measure used for this measure.
|
|
Link/Unlink Objectives... (button)
|
Displays the Link Measures to Objectives
form, which enables you to link the measure to additional scorecards
and objectives.
For details on this form, see How to Link Measures to More Objectives.
|
|
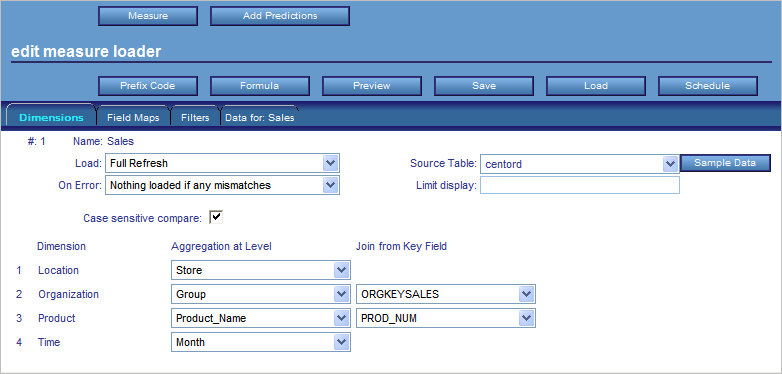
Dimensions
|
The one-character dimension identifier or
identifiers to which the measure is linked. For example, the value
TOP means that the measure is linked to the Time, Organization,
and Product dimensions.
|
|
Measure Loader (button)
|
Available only when the selected measure
is a production measure. Displays the Measure Loader form, which
enables you to design and complete a measure load.
|
|
Measure Type
|
Type of production measure.
|
|
Entry Setup (button)
|
Displays the Edit Measure Entry panel, which
enables you to edit the formulas used in the measure.
|
|
Aggregation Method
|
Method you can use when aggregating this
measure. Choose from Additive, Percentage, Change in Percentage,
or Ratio.
For details, see the Aggregation Method table
entry in How to Create a User-Entered Measure With the New Measure Wizard.
|
|
Threshold/Flex Type
|
The type of value used in the Threshold/Flex
fields:
|
|
Threshold/Flex Direction
|
Direction to be used to determine how thresholding
is performed.
- A - Ascending
(higher is better)
- D - Descending
(lower is better)
- R - Range
(should fall within range)
For more information about
these options, see Indicator Concepts.
|
|
Threshold/Flex
|
In the first field, the value used for the
threshold, which determines the outer range when an indicator shows
red.
In the second field, the value used to determine the
inner edge of the yellow zone. Setting a flex of 0 indicates that
the measure does not allow any deviation from the target.
|
|
Threshold/Flex Slider
|
Displays a grid that enables you to graphically
adjust the threshold and flex values.
|
|
Target
|
Select the type of target you desire.
- Load from
field
- Use fixed
value
- Aggregate
fixed value
When you select Use fixed value or Aggregate
fixed value, the Set Fixed Target Values button appears, which opens
the Fixed Target pop-up dialog box where you can select the desired
target types and enter a target value for each.
|
|
Owner ID
|
The owner ID currently assigned to the measure.
You can select another owner to reassign the measure to that owner
ID.
|
|
Add Predictions
|
Displays the Configure Predictive Data form,
which enables you to select options for predictive data analysis.
|
|
Audit Measures (check box)
|
Select this check box to archive any changes
made to the measure in the PMF measures history table, used for
reporting purposes.
|
|
Access Security (check box)
|
When this check box is selected, data is
filtered using access security at the user's security level.
|
|
Display Format
|
A WebFOCUS numeric display format valid
for the unit of measure. Valid format types are D (floating-point
double-precision), F (floating-point single-precision), I (integer),
and P (packed decimal).
The formats are In, Dn.o,
Fn.o, and Pn.d, where n represents the maximum
number of digits to display, and .o, which is optional, and .d, which
is required, represent the decimal point and the number of digits
to display after the decimal point. The maximum number you can code
before and after the decimal point is 10 for I, 15 for D, 7 for
F, and 31 for P.
For more information about numeric display
options, see the Describing Data With WebFOCUS Language manual.
|
|
Description
|
Intuitive description of the data loaded
into this measure.
|
|
Measure Report
|
From the drop-down list, select an operational
or PMF measure view to which users can automatically drill down.
|
|
Measure Formula
|
You can add a text description of the calculation
method and source fields that you will use in the load procedure
for this measure here. Reports use this field to prompt for actual
values displayed for a measure. This field is useful to explain
to constituents how a measure was calculated.
|

 button.
button.