|
|
|
Creating a Gadget
|
How to: |
For PMF to call a procedure and store parameters locally for a gadget, you must first create a gadget. The gadget enables PMF to manage the gadget. A gadget defines the input parameters for the gadget and controls how the parameters are saved for each user. The class also controls the parameters that each instance of the gadget can store and recall.
|
|
|
Procedure: How to Create a Gadget
Before creating a gadget, add all new gadget procedures to the WebFOCUS pmfgadgets application folder.
- In the Manage page in PMF, click the Gadgets panel button.
- Click New
Gadget.
PMF displays the New Gadget Designer panel. The following image shows the panel, with sample values in the fields.
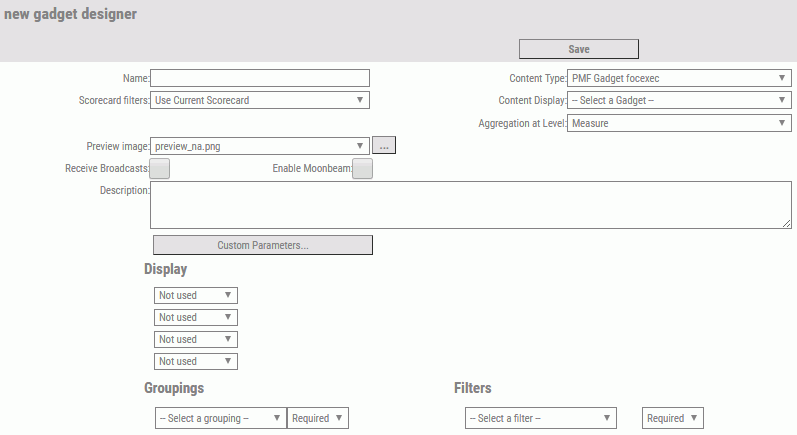
- In the Name field, enter a descriptive name for the new gadget.
- From the Content Type drop-down menu, click the option that applies to the gadget. For details on the choices, see Adding Various Content Types as Gadgets.
- From the
Content Display drop-down menu, click the option that applies to
the gadget.
For example, if the Content Type is PMF gadget focexec, the Content Display drop-down menu contains the names of all FOCEXECs that begin with gadget_ and are in the WebFOCUS pmfgadgets application folder.
- From the
Scorecard filters drop-down menu, click one of the following options.
- Use Current Scorecard, to apply the scorecard that is currently associated with this gadget.
- Scorecard not used, to suppress the use of any scorecard with this gadget.
- From the
Preview image drop-down menu, click the name of the .png file that
supplies the preview image for the gadget.
The preview image appears on the Catalog chevron in Dashboard Designer. If you do not supply a preview image of your own, you can use the default preview image, preview_na.png.
- Select the Receive Broadcasts or Enable Moonbeam check boxes to enable these features for the new gadget.
- In the Description field, optionally type a brief description of the gadget.
- From the available Display, Groupings, and Filters fields, select the applicable options for the new gadget.
- Click Save when
you have finished creating the gadget.
PMF displays a message saying the new gadget has been added. The Gadget Definitions navigation tree on the left is refreshed to display the new gadget.