Access to IMS Through the XMI Server
The XMI server is an application (program XMI) that
intercepts DL/I calls from the Adapter for IMS/DB address space
and issues them to IMS. Before you can invoke the adapter with this
configuration, there must be an XMI server job executing with the appropriate
parameter settings and with an available PCB for the databases you
want to access.
Therefore, access to the XMI server is
a two-part process. The two parts consist of the following:
- Initiating an XMI server.
To initiate an XMI server, you
run a region controller program and pass it parameters that describe
the environment you need. The following chart lists the most common
parameters:
|
Parameter
|
Value
|
Definition
|
|---|
|
Mode
|
BMP
|
Indicates Batch Message Processing mode.
This mode accesses online IMS databases through the IMS/DC address space.
|
|
DLI
|
Indicates local mode. This mode accesses
IMS databases that you allocate locally.
|
|
Program
|
XMI
|
Loads and accesses the XMI server in the
region controller address space. For information on accessing the BMP
extension, see Release Dependent Adapter Features.
|
|
PSB
|
psbname
|
Identifies the PSB to use.
|
One XMI server can service multiple users,
but each user must have a separate PCB. Therefore, to allow multiple
users, the PSB for the server should contain duplicate PCBs.
You
may not have to actually execute this step because if an XMI server
is already running with the correct parameters and an available
PCB, you can use it.
- Invoking the adapter once an XMI server job is running.
XMI server programs can be started at any time. In normal usage,
one such job will be started in the morning with additional jobs
started during the day, as the need for additional PCBs arises.
The job class and time expiration parameters used with the XMI
server job must allow for a long residence in the system, and the
priority should be sufficiently high to give good response to the
users being serviced. In setting the various job parameters that
affect response, remember that these jobs spend most of their time
in the WAIT state consuming no resources, since they have nothing
to do when not responding to DL/I calls. Even when processing such
calls, they only do minimal work. All the logical work of the adapter
is done in the various TSO address spaces.
When you use the XMI server to access IMS databases, you must
allocate a common communication file (to ddname FOCBMP) in both
the FOCUS address space and the XMI server address space. The Communication
File is discussed in Additional Instructions for Using the XMI Server.
This section includes the following topics:
The following sections provide detailed information about the
XMI server, including sample JCL and CLISTs.
xInitiating the XMI Server in BMP Mode: PARM='BMP,XMI,psbname'
BMP (Batch Message Processing) mode accesses online
IMS databases under the control of IMS/DC. Therefore, you can access
Fast Path databases with this configuration, and, if a record is
updated, you retrieve the updated version.
The following diagram illustrates the relationship between FOCUS,
the XMI server, and IMS:
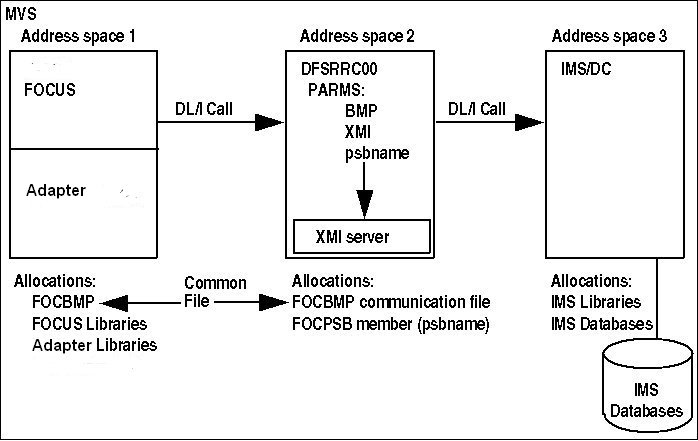
|
Address Space
|
Contains
|
|---|
|
1
|
- FOCUS.
- The Adapter for IMS/DB.
- No IMS components. To communicate with the XMI server, you must
allocate a communication file.
|
|
2
|
- The IMS region controller, DFSRRC00.
- The XMI server.
DFSRRC00 loads the XMI server into its address
space because of the XMI parameter in your JCL. You must allocate
the same communication file here as in the FOCUS address space.
You
must select the PSB prior to your session and pass its name to program
DFSRRC00 as a parameter. This member is the sequential file you
allocate to ddname FOCPSB.
|
|
3
|
|
To initiate an XMI server with this configuration, submit the
following JCL after editing it to conform to your site's standards
and adding a JOB card.
You do not have to submit this JCL if
an XMI server job that has an available PCB is already running with
the following parameter settings
//BMPXMI EXEC
PGM=DFSRRC00,REGION=nn,PARM='BMP,XMI,psbname[,,,,,,,,,nba,oba]'
//STEPLIB DD DSN=IMS.RESLIB,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=prefix.IMS.LOAD,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=prefix.FOCLIB.LOAD,DISP=SHR
//FOCBMP DD DSN=prefix.FOCBMP.DATA,DISP=SHR
//FOCPSB DD DSN=prefix.FOCPSB(psbname),DISP=SHR
//DFSRESLB DD DSN=IMS.RESLIB,DISP=SHR
//ERRORS DD DSN=prefix.ERRORS.DATA,DISP=SHR
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//
where:
- nn
Is the region size.
- psbname
Is the name of the PSB to use.
- nba
Is the number of buffers for the normal buffer allocation.
It is required only for access to Fast Path databases; omit it if
you will not access Fast Path.
Note: There are nine
commas between the psbname and nba parameters.
- oba
Is the number of buffers for the overflow buffer allocation.
It is required only for access to Fast Path databases. Omit it if
you will not access Fast Path.
If
you omit the nba and oba parameters and attempt to access Fast Path databases,
the following message is generated:
(FOC4214) REMOTE DLI CALL ERROR STATUS FOR SEGMENT:XXX/ FR
FR
is an IMS status code indicating that too few buffers were allocated.
- prefix
Is the high-level qualifier for your FOCUS production libraries.
Note:
- IMS.RESLIB is the IMS load library.
- DDNAME FOCBMP is allocated to the common communication file.
You must allocate the same file when you invoke the adapter, as
described in Invoking the Adapter in the XMI Server Environment.
- Most error conditions detected by the XMI server are reflected
back to the originating user, where they are issued to the terminal.
The SYSPRINT file allocated in the XMI server job will contain only
global error messages pertaining to the XMI server environment as
a whole, such as open errors on ddname FOCBMP or FOCPSB.
- PCBs for the XMI server are discussed in Section Additional Instructions for Using the XMI Server.
Once the XMI server job is executing, you can invoke the adapter
from a CLIST or from batch JCL, as described in Section Invoking the Adapter in the XMI Server Environment.
xInitiating the XMI Server in DLI Mode: PARM='DLI,XMI,psbname'
DLI mode accesses IMS databases that you allocate locally
in the DFSRRC00 address space. Since you do not access the IMS/DC
address space, you cannot use Fast Path databases and, if a record
is updated during your session, you cannot retrieve the updated
record.
Note: If you substitute the parameter DBB for DLI, IMS
uses ACBs when accessing databases. This ensures that the database
is in sync with the IMS descriptions you are using.
The following diagram illustrates the relationship between FOCUS,
the XMI server, and IMS:
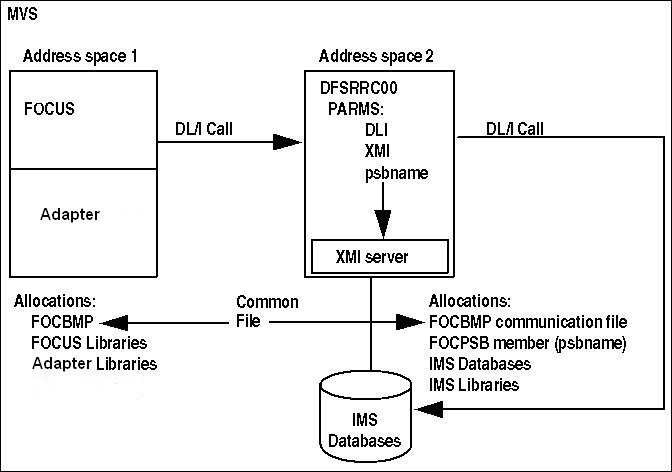
|
Address Space
|
Contains
|
|---|
|
1
|
- FOCUS.
- The Adapter for IMS/DB.
- No IMS components. To communicate with the XMI server, you must
allocate a communication file.
|
|
2
|
- The IMS region controller, DFSRRC00.
- The XMI server.
DFSRRC00 loads the XMI server into its address
space because of the XMI parameter in your JCL. You must allocate
the same communication file here as in the FOCUS address space.
The
DLI parameter that you pass to program DFSRRC00 indicates that the
IMS databases are allocated locally in the DFSRRC00 address space.
You
must select the PSB prior to your session and pass its name to program
DFSRRC00 as a parameter. This member is the sequential file you
allocate to ddname FOCPSB.
|
To initiate an XMI server with this configuration, submit the
following JCL after editing it to conform to the standards at your
site and adding a JOB card. Note that you must allocate your IMS
databases, DBDs, and PSBs in this JCL.
You do not have to submit this JCL if
an XMI server job that has an available PCB is already running with
the following parameter settings
//DLIXMI EXEC PGM=DFSRRC00,REGION=nn,PARM='DLI,XMI,psbname'
//STEPLIB DD DSN=IMS.RESLIB,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=prefix.FOCLIB.LOAD,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=prefix.IMS.LOAD,DISP=SHR
//DFSRESLB DD DSN=IMS.RESLIB,DISP=SHR
//IMS DD DSN=IMS.PSBLIB,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=IMS.DBDLIB,DISP=SHR
//DFSVSAMP DD DSN=IMS.DFSVSAMP(bufpool),DISP=SHR
//PATDB01 DD DSN=IMS.PATIENT.DB,DISP=SHR
//PATDBIX DD DSN=IMS.PATIENT.IX,DISP=SHR
//PATDBIX1 DD DSN=IMS.PATIENT.IX1,DISP=SHR
//PATDBIX2 DD DSN=IMS.PATIENT.IX2,DISP=SHR
//PATDBIX3 DD DSN=IMS.PATIENT.IX3,DISP=SHR
//FOCBMP DD DSN=prefix.FOCBMP.DATA,DISP=SHR
//FOCPSB DD DSN=prefix.IMS.FOCPSB(psbname),DISP=SHR
//ERRORS DD DSN=prefix.ERRORS.DATA,DISP=SHR
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//
where:
- nn
Is the region size.
- psbname
Is the name of the PSB to use.
- prefix
Is the high-level qualifier for your FOCUS production libraries.
- bufpool
Is the member that contains your VSAM buffer pool information.
Note:
- The ddnames allocated to the IMS databases are from the
DD1 parameters in the relevant IMS DBDs. In the sample, the databases
are the PATDB databases and indexes described in Sample File Descriptions.
- IMS.RESLIB is the IMS load library, IMS.DBDLIB is the IMS DBD
library, and IMS.PSBLIB is the IMS PSB library.
- If you specify the parameter DBB instead of DLI on the EXEC
card, you must include the ACB library in the allocation for ddname
IMS. In addition, you must allocate a second data set, IMS.ACBLIB,
to ddname IMSACB.
- Ddname FOCBMP is allocated to the common communication file.
You must allocate the same file when you invoke the adapter, as
described in Invoking the Adapter in the XMI Server Environment.
- Most error conditions detected by the XMI server are reflected
back to the originating user, where they are issued to the terminal.
The SYSPRINT file allocated in the XMI server job will contain only
global error messages pertaining to the XMI server environment as
a whole, such as open errors on ddname FOCBMP or FOCPSB.
- PCBs for the XMI server are discussed in Additional Instructions for Using the XMI Server.
Once the XMI server job is executing, you can invoke the adapter
from a CLIST or from batch JCL, as described in Invoking the Adapter in the XMI Server Environment.
xInvoking the Adapter in the XMI Server Environment
Before you can invoke the adapter in the XMI server
environment, an XMI server job, initiated with the appropriate parameter
settings, must be running and must have an available PCB for each
database you will access. PCBs for the XMI server are discussed in Additional Instructions for Using the XMI Server.
To invoke the adapter interactively,
execute the following CLIST after editing it to conform to the standards
at your site
PROC 0
CONTROL NOMSG
FREE DDNAME(USERLIB ERRORS MASTER FOCEXEC FOCBMP FOCLIB)
ALLOC F(ERRORS) DA('prefix.ERRORS.DATA') SHR REUSE
ALLOC F(USERLIB) DA('prefix.IMS.LOAD' +
'prefix.FUSELIB.LOAD') SHR REUSE
ALLOC F(MASTER) DA('prefix.MASTER.DATA') SHR REUSE
ALLOC F(FOCEXEC) DA('prefix.FOCEXEC.DATA') SHR REUSE
ALLOC F(FOCBMP) DA('prefix.FOCBMP.DATA') SHR REUSE
ALLOC F(FOCLIB) DA('prefix.FOCLIB.LOAD') SHR REUSE
CALL 'prefix.FOCLIB.LOAD(FOCUS)'where:
- prefix
Is the high-level qualifier for your FOCUS production libraries.
To invoke the adapter as a batch job,
submit the following sample JCL after editing it to conform to the
standards at your site and adding a JOB card
//FOCXMI EXEC PGM=FOCUS,REGION=nn
//STEPLIB DD DSN=prefix.FOCLIB.LOAD,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=prefix.IMS.LOAD,DISP=SHR
// DD DSN=prefix.FUSELIB.LOAD,DISP=SHR
//ERRORS DD DSN=prefix.ERRORS.DATA,DISP=SHR
//FOCBMP DD DSN=prefix.FOCBMP.DATA,DISP=SHR
//FOCEXEC DD DSN=prefix.FOCEXEC.DATA,DISP=SHR
//MASTER DD DSN=prefix.MASTER.DATA,DISP=SHR
//SYSOUT DD SYSOUT=*
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//SYSIN DD *
TABLE FILE ...
.
.
.
END
FIN
/*
//
where:
- nn
Is the region size.
- prefix
Is the high-level qualifier for your FOCUS production libraries.
xAdditional Instructions for Using the XMI Server
This section explains how to allocate the common communication
files needed for the XMI server, how to create PSBs for use with
the XMI server, and how to terminate XMI server jobs.
x
The "handshake" between the adapter, running in its
address space (or as a batch job), and XMI, running in another address
space, requires a communication file accessible to both. This file
must be allocated to ddname FOCBMP. It consists of a single 16-byte
record, and it plays no role in subsequent message traffic between
the two programs. Space for this file must be allocated once (on
a permanently mounted disk pack) and catalogued as part of the installation
of the XMI server (see Installation Instructions).
The data set name is irrelevant.
Note: The following discussion assumes that the FOCUS
production libraries are stored in data sets catalogued under the
same high-level qualifier. The identifier prefix denotes
this common high-level qualifier.
After the communication file has been created, when you subsequently
invoke the adapter and the XMI server, allocate this file as follows:
From TSO, you can allocate the FOCBMP file any time before you
first attempt to use it, in the logon procedure, from a CLIST executed
before you enter FOCUS, or from within the session.
When several concurrent XMI jobs are active, each one requires
its own communication file. Each XMI server job must allocate a
different file, it does not matter which one, to ddname FOCBMP.
For example, XMI job 1:
//FOCBMP DD DSN=prefix.FOCBMP.DATA,DISP=SHR
XMI job 2:
//FOCBMP DD DSN=prefix.FOCBMP1.DATA,DISP=SHR
Every TSO ID must allocate all of
the communication files corresponding to the XMI jobs it might want
to use. Each communication file must be allocated to a different
but standard ddname. These ddnames are FOCBMP, and FOCBMP1 through
FOCBMP15. For example:
DYNAM ALLOC FILE FOCBMP DA prefix.FOCBMP.DATA SHR
DYNAM ALLOC FILE FOCBMP1 DA prefix.FOCBMP1.DATA SHR
It does not matter how the communication files and the FOCBMP
ddnames are paired. For example, if two XMI server jobs are active,
the user can allocate their files to any two of the sixteen standard
ddnames.
In the interest of simplicity, each user should allocate all
of the communication files that were created at installation time,
even if the corresponding XMI jobs may not be active. This technique
makes it possible to use a common CLIST for these allocations.
If none of the FOCBMP files are allocated, the adapter does not
attempt to use the XMI server. It issues its own DL/I calls instead.
These DL/I calls will be successfully transmitted to IMS only if
your environment is configured as described in Access to IMS With FOCUS Loaded by the Region Controller.
x
Since IMS uses the PCB to maintain the position of an
application program in the database, concurrent users who are serviced
by the same XMI job cannot share PCBs.
Each user application that accesses the server queries all the
XMI jobs to which it is linked through the communication files,
until it finds one that has a free PCB appropriate for reporting
on the database. (The search for an available PCB is transparent
to the user.) The PCB remains occupied for the duration of the retrieval
portion of a request and is freed prior to the output portion of
the request.
Thus, if ten users need concurrent access to the SALES database,
the PSB must contain at least ten PCBs that correspond to the Master
File for SALES. The eleventh user will receive a diagnostic message
indicating that there is no free PCB available at the time. (In
this case, the user should initiate another XMI server, as illustrated
in previous sections.)
The ten SALES PCBs can reside in one of the following:
- In a single PSB that requires only one XMI job.
- In ten identical PSBs with one SALES PCB each for ten concurrent
XMI jobs.
- In any other combination that adds up to ten.
The IMS DBA must determine which configuration is best for the
site. The tradeoff is between a single large PSB that ties up only
one XMI region or several XMI regions, each running a non-duplicated
and, therefore, smaller PSB.
Note: If the PSB contains multiple PCBs for the same database,
in order to allow access through secondary indexes, you must duplicate
the whole block of PCBs. IMS Overview and Mapping Concepts and Creating FOCUS Descriptions describe
secondary index PCBs.
x
Terminating an XMI Server
A successfully started XMI server job will not end automatically.
The operator must terminate it in one of three ways:
Termination through job XMIKILL avoids problems. The job sends
the server a termination message that breaks into the server message
queue ahead of all other messages addressed to it. Upon receipt
of this message, the server performs its cleanup and returns to
IMS, signaling a normal completion.
Sample JCL for job XMIKILL follows
//XMIKILL EXEC PGM=FOCUS,REGION=nn
//STEPLIB DD DSN=prefix.FOCLIB.LOAD,DISP=SHR
//ERRORS DD DSN=prefix.ERRORS.DATA,DISP=SHR
//SYSOUT DD SYSOUT=*
//ddname DD DSN=comfile,DISP=SHR
//FOCEXEC DD DSN=prefix.FOCEXEC.DATA,DISP=SHR
//SYSPRINT DD SYSOUT=*
//SYSIN DD *
EX XMI ACTION=STOP,GATEWAY=FOCBMP
FIN
/*
//
where:
- nn
Is the region size.
- prefix
Is the high-level qualifier for your FOCUS production libraries.
- ddname
Is the ddname allocated to the communication file of the
XMI server job to be terminated. If only one job is to be terminated,
use ddname FOCBMP.
- comfile
Is the data set name of the communication file that is allocated
to the XMI server job you want to terminate; for example, 'prefix.FOCBMP.DATA'.
Any of the three termination methods can be invoked at any time,
without impact on those who might be actively using the canceled
job (except for the impact on IMS/DC discussed previously). All
such users will receive one of several error messages, depending on
where in their retrieval process the cancellation occurred. Their
retrieval ends cleanly. In no case will the user ABEND or be left
with a hung terminal.

