Configuring Workspace Manager
The Workspace Manager is the component of the Reporting Server
that is responsible for managing all server administrative tasks.
These tasks, generally performed by Server Administrators, include
monitoring server activity, configuring and adjusting the server configuration
profile, adding users, enabling and creating services, defining
deferred execution characteristics, and enabling and disabling e-mail
alerts.
The Server Administrator responsible for the installation, configuration,
security, and maintenance of the server uses the Workspace Manager
to keep the server available to clients and running at peak efficiency.
To use the Workspace Manager, open Internet Explorer and navigate
to the HTTP port on the host machine where the Server is running.
Your Server must be running in order for you to use the Workspace
Manager.
Tip: This chapter references a number of Workspace
related keywords. Within the help system, you can access detailed
information about these keywords by clicking the keyword links in
this document. You can also click the ? icon
next to parameters on the Workspace configuration panes.
xWorkspace Manager Configuration Privileges
Access to the administrative features of the Web Console can
be restricted by defining a list of users in the admin id and
storing the list in a release independent file called admin.cfg.
This file is located, by default, in .../ibi/profiles.
The list of users and user roles defined in admin.cfg defines
a list of administrators that can be used for authorization and/or
authentication according to established security. Administrators
are responsible for installing, configuring, and maintaining the
Server with varying degrees of responsibility, depending on their
administration levels (SRV, APP, OPR). At least one administrator
must be defined in the list, although most sites identify other persons
to act as backups.
For example, a Server Administrator (SRV) can perform all the
administrative tasks available through Web Console operations. If
more than one Server Administrator is defined, the first valid member
on the list is used to impersonate FOCUS Database Server (FDS) and other
special services. An Application Administrator (APP) is limited
to the administrative tasks that do not require changing configuration
or restarting the server. Both Server Administrators and Application
Administrators can edit user profiles in the user.prf file. However,
Server Administrators can edit all user.prf files, while Application
Administrators can only edit their own profiles.
Any IDs (beyond the original ID used to configure the server)
that are used for server or application administration require read/write
privileges to the respective locations that the IDs are expected
to manage. To assign these privileges, you must establish group
rights for the locations at the operating system level. To view
and run Resource Governor procedures, for example, IDs must be at
least at the Application Administrator level.
xEmitting a Custom Message From a Quiesced Server
A server administrator can enter a custom message that
will be displayed for a new user connection to the server when the
server is in Quiesce mode.
x
Procedure: How to Set a Custom Message for a Quiesced Server
To
define a custom message that will be delivered from a quiesced server:
-
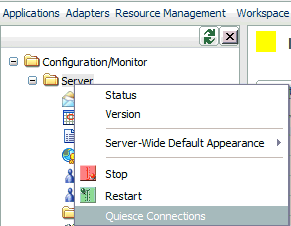
From the Workspace menu,
select Configuration/Monitor.
-
In the navigation
pane, right-click the Server folder and
select Quiesce Connections.
-
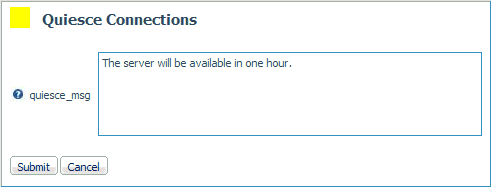
Enter the
message in the quiesce_msg field.
-
Click Submit.
You will be asked if you want to disable new connections.

-
Click OK.
Note: This
feature is only available to a user having server admin privileges.
xConfiguring an Agent Service
A server configuration requires
at least one agent service with the name DEFAULT, defined by a SERVICE block.
An agent service is an entity used to define the parameters for
a group of data access agents, so that a configuration can manage
different groups of data access agents for different purposes. Each
data access agent runs for a specific Data Service, and each service
may have different values for the settings defined on the services
configuration panes. These settings include:
xConfiguring Deployment Modes
The deployment
mode of a service defines how data access agents are assigned
to connections:
- In private deployment,
a dedicated application agent is assigned for each connection request.
Private deployment retains the behavior of all prior server releases. At
connect time, global, as well as user and service level profiles,
are executed. At disconnect time, all temporary files are removed
and database connections are closed. The privileges of each application
agent depend on the security mode of the server.
With security
set to a value other than OFF, authentication is processed for every client
logging on to the server. With security OFF, user identification
and authentication are not required. The effective user ID becomes
the connecting user for the duration of the session.
- In connection_pooled
deployment, the global profile and service profiles are executed
when an agent is started, and pooled user profiles are executed
on each connection. The WebFOCUS context is cleared once the session
is established for a new connection, and then the pooled user profile
is executed.
With security set to a value other than OFF, all
users have the same rights because the effective pooled user is
unique, regardless of the connecting user.
Connection
pooled deployment provides significant performance advantages and is
recommended when a large number of users share the same operating
system and DBMS credentials. It cannot be used when each connecting
user has specific operating system and DBMS rights, nor can it be
used for the service DEFAULT with the server security mode set to
DBMS because, in this situation, the profile is disabled for connection
authentication.
x
Procedure: How to Set the Server Deployment Parameter in a Server Profile
To set the server configuration
parameter deployment:
-
From the Workspace menu,
select Configuration/Monitor.
-
In the navigation
pane, right-click the Data Services folder,
and select New.
The New Data Service page opens.
Tip: For an existing service
(for example, DEFAULT, WC_DEFAULT, DMC_DEFAULT, DEFAULT_CPOOL),
right-click the service and choose Properties from
the menu to open the Services pane.
-
In the deployment
field, choose: private or connection_pooling.
-
With private deployment, all profiles are executed on
connection. On disconnect, all DBMS connections are dropped. This
is the default value.
With security set to a value other than
OFF, the effective user ID is switched to the connecting user
for the duration of the connection.
Skip
to step 6.
-
With connection-pooled deployment, the global profile and
service profiles are executed when an agent is started, and pooled
user profiles are executed on each connection. The WebFOCUS context
is cleared once the session is established for a new connection,
and then the pooled user profile is executed.
When you select
this option, pooled_user and pooled_password are
displayed.
With security set to a value other
than OFF, all users have the same rights because the effective
user is unique (configured using pooled_user and pooled_password)
regardless of the connecting user.
Continue
with steps 4 and 5.
-
Select the pooled
user from the drop-down list. (This list is populated
from the admin.cfg file described in Workspace Manager Configuration Privileges.)
This service level keyword is required
for connection_pooling deployment with security mode OPSYS. It defines
the user ID under which all agents will run. The DBMS user IDs are
determined by the connection setting type.
-
Enter the
corresponding password. Note that pooled
password is only required for connection_pooling deployment on Windows operating
systems.
-
Click the Save button.
xConfiguring for Deferred Management
You can configure the settings that are used to manage deferred
requests and reports from the Web Console Deferred Configuration
pane. Deferred management parameters are stored in the edaserve.cfg
file.
x
Procedure: How to Set Deferred Management Properties
-
From the Workspace menu,
select Configuration/Monitor.
-
In the navigation
pane, expand the Special Services and Listeners folder.
-
Right-click DFM,
and select Properties.
The DFM Scheduler Configuration page opens.
-
To set properties
for the deferred execution of requests, enter values for the following
options:
-
dfm_dir
-
Defines the location where deferred
requests and responses are stored. For related information, see Extensions for Deferred Files.
-
dfm_int_min
-
Defines the minimum time interval that
the DFM listener sleeps between handling two requests.
-
dfm_int_max
-
Defines the maximum time interval that
the DFM listener sleeps between handling two requests
-
dfm_maxage
-
Defines the maximum number of days
that deferred reports are kept in the server after they are created.
-
dfm_maxoutput
-
Defines the maximum size of a deferred
report expressed as the number of kilobytes [K] or megabytes [M]
between 0 and 65535, where 0 means unlimited. Kilobytes is the default.
Reports that over this limit are removed.
x
Procedure: How to View Deferred Process Statistics
-
From the Workspace menu,
select Configuration/Monitor.
-
In the navigation
pane, expand the Special Services and Listeners folder.
-
Right-click DFM,
and select Statistics.
The Statistics
page displays the following information in the General section:
- Name: DFM
- Remark
- Status
- Process ID
The Statistics page displays
the following information in the System section:
- PageFaultCount
- PeakWorkingSetSize
(KB)
- WorkingSetSize (KB)
- QuotaPeakPagedPoolUsage
- QuotaPagedPoolUsage
- QuotaPeakNonPagedPoolUsage
- QuotaNonPagedPoolUsage
- PagefileUsage
- PeakPagefileUsage
- Total Execution Time
- Port Number
The Statistics page displays
the following information in the Connection section:
- DFM_DIR Available
Disk Space (KB)
- Number of Requests
Done Since Startup
- Number of Response
Ready
For more information, see Statistics for an Individual Special Service.
x
Reference: Extensions for Deferred Files
The following table lists possible extensions for the
deferred files listed in the dfm_dir directory.
|
Extension
|
Description
|
|---|
|
REQ
|
Request file.
|
|
RQD
|
Data file. Contains
user ID, optional flags, and so on.
|
|
RQP
|
Request is being executed.
|
|
RQF
|
Request is waiting
to be executed.
|
|
DEL
|
Request is deleted.
|
|
RSP
|
Response file. Contains
the whole report for one request.
|
|
RPF
|
Response is ready.
|
|
RPE
|
Response exceeds maximum
limit.
|
xQueuing User Connections After the Maximum Limit Is Reached
The max_connections_per_user
property for a Data Service specifies the maximum number of connections
to the Data Service allowed for each user. When a user exceeds the maximum
number allowed, additional connections requested by that user are
rejected, and the server displays the message
Connection refused due to the max_connections_per_user (n)
being exceeded
where n is the number of allowed connections.
You have the option to queue user connections that are refused
by the server, using the queue_max_user_conns property on the Data
Service Properties page. That option is available only if the Queuing
property for the Data Service is On.
x
Procedure: How to Queue User Connections to a Data Service
-
On the Web
Console menu bar, click Workspace, then Configuration/Monitor.
-
In the Configuration/Monitor
navigation tree, expand the Data Services folder.
-
Right-click
the service for which you want to queue user connections, for example, DEFAULT.
-
From the
menu, click Properties.
The Properties page for the selected Data
Service opens.
-
In the Queuing
field, click on from the drop-down list.
-
In the max_connections_per_user
field, type the maximum number of connections allowed for each user.
-
In the queue_max_user_conns
field, click y from the drop-down list to
enable the queuing of connections that exceed the number specified
in the max_connections_per_user field.
In the following image, Queuing is turned
on, max_connections_per_user is set to 3, and queue_max_user_conns
is enabled.

-
Click Save to
save the new settings. You must restart the server for the settings
to take effect.



