The Manage Privileges dialog box is available by right-clicking an application directory, or an object, such as a procedure or synonym, and selecting Privileges.
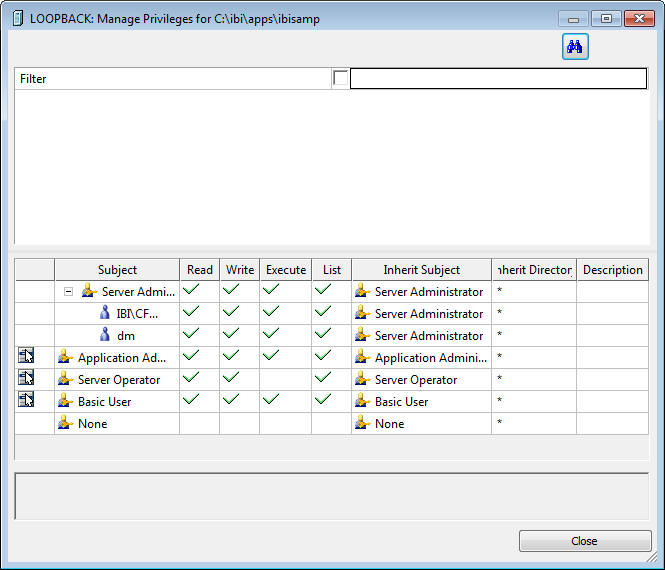
The Manage Privileges dialog box has the following columns:
- Edit
-
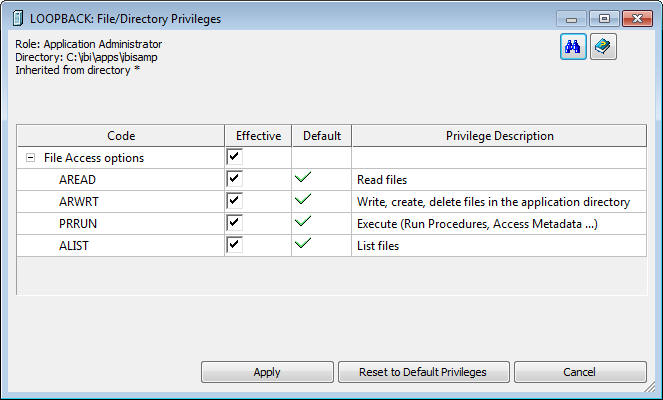
Privileges can be edited by double-clicking the line, or right-clicking and selecting Edit Privileges.
The File/Directory window opens, as seen in the following image. The options in the Effective column that are selected will be applied to the selected file when you click Apply.
- Subject
-
This column shows roles, users, and groups.
- Roles
-
There are five roles that can be used for managing privileges. Additional roles can be added by the server administrator. The default roles are:
- Server Administrator. Has full control of the workspace, adapters, synonyms, and procedures.
- Application Administrator. Can create synonyms and procedures, and run them.
- Server Operator. Can start and stop the server, as well as monitor and kill agents.
- Basic User. Can execute procedures.
- None. Has no privileges.
- Users and Groups
-
Each role can have users or groups of users associated with it. These are shown indented under each role name.
- Privileges
-
The privileges that are associated with each directory Orville are:
- Read. The user can read the directory or file.
- Write. The user can write, create, edit, or delete the directory or file.
- Execute. The user can run procedures or access metadata.
- List. Lists files.
- Inherit Subject
-
Shows if the privileges are inherited from those of a directory by showing that directory.
- Description
-
The description for the directory or file, if any.