Logging FOCUS Database Server Activity in HLIPRINT
FOCUS can record all user activity on the FOCUS Database
Server in a sequential file. Each HLI command is a single action.
Each MODIFY/Maintain transaction or TABLE request may execute a
series of actions, such as database opens and closes, reads, key
matches, and value changes. When you use the ECHO option, the sequential
file (allocated to ddname HLIPRINT) records:
- Each user action.
- The database for which the action took place.
- The database segment read or modified by the action.
- The batch job or user ID that issued the action.
You can generate an extended form of the HLIPRINT file by using
the STAT option. In addition to the information displayed by the
ECHO option, the extended form lists the following:
- The date and time of the action.
- The amount of CPU time it took to execute the action.
- The number of I/O operations required to execute the action.
- For FOCUS users, the name of the FOCUS procedure (FOCEXEC) executing
the action (or a blank field for interactive commands).
- For MODIFY/Maintain requests using Case Logic, the name of the
case executing the action or a blank field for non-case logic procedures.
The HLIPRINT file has three uses:
- It provides a guide for restarting procedures that end prematurely.
The restart must be tailored to each application, however, as the
HLIPRINT file does not log transaction data.
- It provides a means for usage accounting based on the number
of actions taken and on the amount of resources consumed.
- It provides a means for monitoring resource utilization, particularly
during testing of new procedures.
xHLIPRINT File Contents (Simple Format)
The following is a sample of the HLIPRINT file generated
with the ECHO option. A description of the columns follows.
CMD FILENAME STATUS NEWSEG TARGET ANCHOR NTEST USERID REF NUMB
OPN FOCUSSU 0 WIBDIW 00000001
RD CAR 0 1 WIBDIW 00000002
OPN CAR 0 WIBEFO 00000003
MINT CAR 0 WIBEFO 00000004
MATA CAR 0 ORIGIN WIBEFO 00000005
MATB CAR 0 COMP WIBEFO 00000006
MDEL CAR 0 COMP WIBEFO 00000007
MATB CAR 0 ORIGIN WIBNNR 00000008
MATB CAR 1 COMP WIBNNR 00000009
MINC CAR 0 COMP WIBNNR 00000010
MATB CAR 0 ORIGIN WIBMHK 00000011
MATB CAR 0 COMP WIRMHK 00000012
MDEL CAR 0 COMP WIBMHK 00000013
MATB CAR 0 ORIGIN WIBEFO 00000014
MATB CAR 1 COMP WIBEFO 00000015
MINC CAR 0 COMP WIBEFO 00000016
MATB CAR 0 ORIGIN WIBNNR 00000017
MATA CAR 0 COMP WIBNNR 00000018
MINC CAR 1 COMP WIBNNR 00000019
CLO CAR 0 WIBNNR 00000020
CLO FOCUSSU 0 WIBNNR 00000021
The columns in the chart are:
- CMD
The type of action:
- OPN
Open a file.
- RD
Read a page from a FOCUS database.
- MINT
MODIFY/Maintain/SU initialization.
- MATA/MATB/MATC/MATD
Match a field value or values in the database (MODIFY/MAINTAIN
MATCH subcommand).
- MUPD
Update a segment instance (MODIFY/Maintain UPDATE subcommand).
- MDEL
Delete a segment instance and its descendents (MODIFY/Maintain
DELETE subcommand).
- MNEX
Move to the next segment instance in the segment chain (MODIFY/Maintain TEXT
subcommand).
- MREP
Move to the first segment instance in the segment chain (MODIFY/Maintain REPOSITION
subcommand).
- MCMT
COMMIT subcommand.
- MRBK
ROLLBACK subcommand.
- SAV
Write transactions from buffer to the database
- CLO
Close a file.
Any other action
in this column is an HLI command issued when using HLI with SU.
- FILENAME
The ddname of the centrally controlled database on which
the action took place. Note that the FILENAME column in the sample
HLIPRINT file lists a file allocated to ddname FOCUSSU. This is
a FOCUS work file.
- STATUS
Contains either the value of the FOCURRENT variable or the
HLI status code for the action. If the action ended normally, this
value is set to 0. If a MATCH command failed to locate a segment
instance (ON NOMATCH condition), or if a NEXT command reached the
end of a segment chain (ON NONEXT condition) this value is set to
1. Otherwise, it is the FOCURRENT field or the HLI status code for
the action. For a list of the HLI status codes, see HLI Status Codes Returned in FCB Word 24.
- NEWSEG
The name of the first segment of new information (for HLI
only).
- TARGET
The segment read or modified by the action.
- ANCHOR
The anchor segment (for HLI only).
- NTEST
The number of test conditions qualifying a retrieved record.
For FOCUS users, the number of the database page that was read by
an RD action. A page for a FOCUS database is a 4096-byte physical
record. A page for an XFOCUS database is a 16K-byte physical record.
- USERID
The TSO user ID or job ID that issued the action.
- REF NUMB
The action number in the HLIPRINT file. REF NUMB is useful
with the FOCUS ? FILE command. This query displays a chart showing
when each segment in a FOCUS database was last changed (this command
is described in the Developing Applications manual).
The last column in that chart, LAST TRANS NUMBER, lists a number
for each segment in the file. If the file was last modified under
SU, these numbers refer to the REF NUMB column in the HLIPRINT file,
pointing to the last action performed on the segment (usually a
CLO or SAV action).
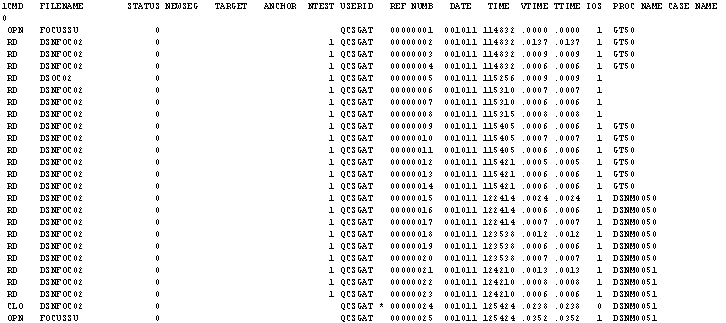
xHLIPRINT File Contents (Extended Format)
The following figure shows a sample extended HLIPRINT
file. The columns are the same as those in the HLIPRINT file described
in HLIPRINT File Contents (Simple Format),
with the additions described following the sample. If you display
the file on a system editor, note that the first column is reserved
for print control characters.
A Master File is supplied for the extended HLIPRINT file (member
HLIPRINT in MASTER.DATA on the distribution tape). This enables
you to write FOCUS reports against the file. For details on producing
these reports, see Producing HLIPRINT Reports.
- DATE
-
Date the action was executed, in YYMMDD (year, month, day)
format.
- TIME
-
Time the action finished execution, in HHMMSS (hours, minutes,
seconds) format.
- VTIME
-
Total elapsed CPU time for executing the action (as indicated
in the ASCBEJST field of the ASCB for the FOCUS Database Server).
If the action took longer than 99.99 seconds to execute, VTIME displays
a value of 99.99. Note that the value of VTIME is .0000 for the
first action after the server was started.
- TTIME
-
Same as the VTIME column.
- IOS
-
Number of database input/output (I/O) operations performed
to complete the action. This number reflects only I/O operations
on FOCUS or XFOCUS databases and does not include I/O operations
on other files such as Master Files. If the action required more
than 9999 I/O operations, IOS displays a value of 9999.
- PROCNAME
-
For FOCUS users, the name of the FOCUS procedure (FOCEXEC)
executing the action. For users issuing FOCUS commands live on the
terminal, PROCNAME is blank.
For HLI users, the contents of
FCB words 7 and 8. SU does not use words 7 and 8, so HLI users can
define their own contents for these words and have them displayed in
the PROCNAME column.
- CASE NAME
-
For MODIFY/Maintain requests only.
If the request defines a temporary
field called SUPRINTNAME (pronounced SU print name), it is the value
of this field. SUPRINTNAME must be an alphanumeric field no longer
than 12 characters. For example, if your MODIFY/Maintain request
contains the following command, the CASE NAME column will display
the value MARK until the next COMPUTE command places another value
in the SUPRINTNAME field:
COMPUTE SUPRINTNAME/A12 = 'MARK';
If
the request does not define SUPRINTNAME but uses Case Logic, this
contains the name of the case that executed the action. Otherwise,
CASE NAME is blank.
xCreating and Using an HLIPRINT File
To record activity in the HLIPRINT file, follow these
instructions when starting the FOCUS Database Server:
- When recording the HLIPRINT file on disk or tape, make sure
there is adequate storage space for the file. HLIPRINT files can
grow very quickly. A single MODIFY/Maintain transaction or TABLE
command can generate several actions and several lines of output,
so a day's use can produce thousands of lines. When the space reserved
for HLIPRINT is exhausted, the FOCUS Database Server cannot recover.
- Allocate the HLIPRINT file in the startup JCL for the server.
Give the file the following characteristics:
- For simple HLIPRINT
files (the ECHO option): records are fixed-length and blocked format
(RECFM=FB), with a length of 88 characters (LRECL=88), and the block
size must be some multiple of 88 (for example, BLKSIZE=8800).
- For extended HLIPRINT files (the STAT option): records are fixed-length
and blocked (RECFM=FB), with a length of 133 characters (LRECL=133).
The block size must be a multiple of 133 (for example, BLKSIZE=1330).
- In general, the larger the block size, the fewer I/O operations
FOCUS has to perform. Keep in mind, however, that if the FOCUS Database
Server terminates abnormally, all records on the last unwritten
block are lost.
Give HLIPRINT the following disposition:
- Use NEW for a new file.
- Use OLD for existing files if you want the new output to replace
the present file contents.
- Use MOD for existing files when you want to append new output
to the existing file contents.
The following is a sample
DD card for allocating a new file using the simple format:
//HLIPRINT DD DSN=SULOG.DATA,
// DCB=(LRECL=88,BLKSIZE=8800,RECFM=FB),
// DISP=(NEW,CATLG),UNIT=SYSDA
This DD
card allocates a new file for the extended HLIPRINT format:
//HLIPRINT DD DSN=SULOG.DATA,
// DCB=(LRECL=133,BLKSIZE=13300,RECFM=FB),
// DISP=(NEW,CATLG),UNIT=SYSDA
This DD
card allocates an existing file with the new output appended to
the present file contents:
//HLIPRINT DD DSN=SULOG.DATA,DISP=MOD,DCB=...
The
HLIPRINT file can be allocated to tape, disk, or a SYSOUT queue.
- Use the following EXEC card in the FOCUS Database Server JCL
to execute the HLISNK program:
//HLISNK EXEC PGM=HLISNK, PARM={'password ECHO'|'password STAT'}where:
- ECHO
Records activity in a simple HLIPRINT file.
- STAT
Records activity in an extended HLIPRINT file.
- password
The password is optional. If you choose to omit it, remember
to type a leading blank before the ECHO or STAT keyword. Otherwise,
FOCUS will not interpret it correctly.
xProducing HLIPRINT Reports
The extended HLIPRINT log facility
has an associated Master File called HLIPRINT. This enables you
to produce summary reports of your HLIPRINT log information using
FOCUS TABLE commands. These summary reports can be used to:
- Determine peak FOCUS Database Server
usage by user, time of day, database, or application.
- Troubleshoot performance problems in procedures or database
design.
- Perform usage accounting.
Before you can issue TABLE commands against HLIPRINT, you must
allocate ddname HLIPRINT to the log file. If you named your HLIPRINT
data set MYTRACE.HLIPRINT.DATA, you would issue the following command
from within FOCUS:
TSO ALLOCATE F(HLIPRINT) DA('MYTRACE.HLIPRINT.DATA') SHRYou must also allocate ddname MASTER to the Master File PDS supplied
with FOCUS.
After allocating HLIPRINT and MASTER, you can issue TABLE requests
against the HLIPRINT file.
The following sample request determines how much of the server
resources were used by each user ID:
TABLE FILE HLIPRINT
SUM CPU AND IOS
BY USERID
END
This request produces a report showing the total elapsed job
step time and the number of I/O operations used by the sink machine
on behalf of each user ID.
The next sample request can be used to locate performance problems
in an application:
TABLE FILE HLIPRINT SUM CPU AND IOS
BY PROC_NAME BY CASE_NAME ON PROC_NAME SUMMARIZE
END
The output is:
PROC_NAME CASE_NAME CPU IOS
--------- --------- ----- ---
CARLOAD .3204 6
*TOTAL CARLOAD .3204 6
CARMOD ADDCASE 1.1040 17
DELCASE .5919 10
LOCATE 19.8299 428
SHOWCASE 1.2534 5
TOP .5745 6
UPDATECASE 1.1790 21
*TOTAL CARLOAD 24.5327 487
TOTAL 24.8531 493This report shows that case LOCATE in the procedure CARMOD consumes
most of the CPU time and I/O resources. This particular part of
the application could probably be redesigned to run more efficiently.
For more information about report requests, see your FOCUS documentation.
