Reference: COUNTER Iterator Properties
|
Property Name |
Allowable Value |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Iterations |
A numeric expression, constant, XPath, or variable. |
Number of times this iterator loop is to be repeated. |
|
Interim document type |
A literal, variable, or XPath that evaluates to "original" or "transient." |
Determines whether the document passed out of the Iterator object into the loop is the original or the result of the previous iteration (transient). |
|
Output document type |
A literal, variable, or XPath that evaluates to "original" or "transient", or "status." |
Determines whether the document passed out of the Iterator object upon completion of the loop is the original or the result of the previous iteration (transient). |
Example: Counter Iterator Type
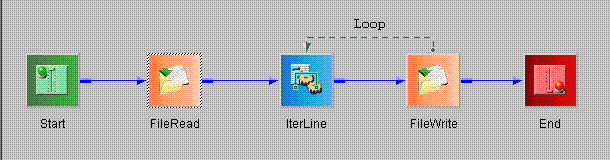
The com.ibi.agents.XDIterCount operator repeats the body of the loop a specified number of times. The number can be constant or computed at run time, for instance, with an XPath expression, as in this example. The inner part of the loop can be used to generate multiple outputs, read multiple inputs from a source, or perform any other operation repeatedly. The count iterator can also be used with conditional logic to add retry functionality to an adapter that does not natively support retry. The number of iterations of the loop is not dependent on the structure of the input document, nor does the count iterator parse the document before injecting it into the loop.
The Iterator object in this example passes the input document into the loop the number of times specified by the <count> XML tag in the input document. The following sections show the process flow, the Iterator object parameters, and the input and output documents of this example.
Process Flow Diagram
Iterator Object Parameters
Input Document
<IterCountTest> <count>3</count> </IterCountTest>
Output Document(s)
Three documents are output by the FileWrite object: IterCount01.xml, IterCount02.xml, and IterCount03.xml.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-16"?> <IterCountTest> <count>3</count> </IterCountTest>