Reference: Usage Notes for DB_INFILE
- If both the source and target data sources have MISSING=ON for a comparison field, then a missing value in both files is considered an equality. If MISSING=OFF in one or both files, a missing value in one or both files results in an inequality.
- Values are not padded
or truncated when compared, except when comparing date and date-time
values.
- If the source field is a date field and the target field is a date-time field, the time component is removed before comparison.
- If the source field is a date-time field and the target field is a date field, a zero time component is added to the target value before comparison.
- If an alphanumeric field is compared to a numeric field, an attempt will be made to convert the alphanumeric value to a number before comparison.
- If FOCUS processes the comparison, and the target data contains characters that FOCUS considers wildcard characters, it will treat them as wildcard characters unless the command SET EQTEST = EXACT is in effect.
Example: Comparing Source and Target Values Using an SQL Subquery File
This example uses the WF_RETAIL DB2 data source.
The SQL file named retail_subquery.sql contains the following subquery that retrieves specified state codes in the Central and NorthEast regions:
SELECT MAX(T11.REGION), MAX(T11.STATECODE) FROM wrd_dim_geography T11 WHERE (T11.STATECODE IN('AR', 'IA', 'KS', 'KY', 'WY', 'CT', 'MA', 'NJ', 'NY', 'RI')) AND (T11.REGION IN('Central', 'NorthEast')) GROUP BY T11.REGION, T11.STATECODEThe retail_subquery.mas Master File follows:
FILENAME=RETAIL_SUBQUERY, SUFFIX=DB2 , $
SEGMENT=RETAIL_SUBQUERY, SEGTYPE=S0, $
FIELDNAME=REGION, ALIAS=E01, USAGE=A15V, ACTUAL=A15V,
MISSING=ON, $
FIELDNAME=STATECODE, ALIAS=E02, USAGE=A2, ACTUAL=A2,
MISSING=ON, $The retail_subquery.acx Access File follows:
SEGNAME=RETAIL_SUBQUERY, CONNECTION=CON1, DATASET=RETAIL_SUBQUERY.SQL, $
Note: You can create an SQL subquery file, along with a corresponding synonym, using the HOLD FORMAT SQL_SCRIPT command. For more information, see the Creating Reports manual.
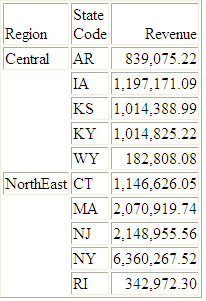
The following request uses the DB_INFILE function to compare region names and state codes against the names retrieved by the subquery:
TABLE FILE WFLITE
SUM REVENUE
BY REGION
BY STATECODE
WHERE DB_INFILE(RETAIL_SUBQUERY, REGION, REGION, STATECODE, STATECODE)
ON TABLE SET PAGE NOPAGE
ENDThe trace shows that the subquery was inserted into the WHERE predicate in the generated SQL:
SELECT
T11."REGION",
T11."STATECODE",
SUM(T1."Revenue")
FROM
wrd_fact_sales T1,
wrd_dim_customer T5,
wrd_dim_geography T11
WHERE
(T5."ID_CUSTOMER" = T1."ID_CUSTOMER") AND
(T11."ID_GEOGRAPHY" = T5."ID_GEOGRAPHY") AND
((T11."REGION", T11."STATECODE") IN (SELECT MAX(T11.REGION),
MAX(T11.STATECODE) FROM wrd_dim_geography T11 WHERE
(T11.STATECODE IN('AR', 'IA', 'KS', 'KY', 'WY', 'CT', 'MA',
'NJ', 'NY', 'RI')) AND (T11.REGION IN('Central', 'NorthEast'))
GROUP BY T11.REGION, T11.STATECODE))
GROUP BY
T11."REGION",
T11."STATECODE "
ORDER BY
T11."REGION",
T11."STATECODE "
FOR FETCH ONLY;
END The output is:
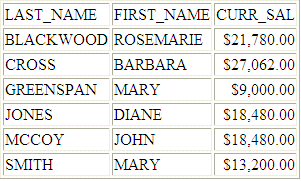
Example: Comparing Source and Target Values Using a Sequential File
The empvalues.ftm sequential file contains the last and first names of employees in the MIS department:
SMITH MARY JONES DIANE MCCOY JOHN BLACKWOOD ROSEMARIE GREENSPAN MARY CROSS BARBARA
The empvalues.mas Master File describes the data in the empvalues.ftm file
FILENAME=EMPVALUES, SUFFIX=FIX , IOTYPE=BINARY, $
SEGMENT=EMPVALUE, SEGTYPE=S0, $
FIELDNAME=LN, ALIAS=E01, USAGE=A15, ACTUAL=A16, $
FIELDNAME=FN, ALIAS=E02, USAGE=A10, ACTUAL=A12, $
Note: You can create a sequential file, along with a corresponding synonym, using the HOLD FORMAT SQL_SCRIPT command. For more information, see the Creating Reports manual.
The following request against the FOCUS EMPLOYEE data source uses the DB_INFILE function to compare employee names against the names stored in the empvalues.ftm file:
FILEDEF EMPVALUES DISK baseapp/empvalues.ftm TABLE FILE EMPLOYEE SUM CURR_SAL BY LAST_NAME BY FIRST_NAME WHERE DB_INFILE(EMPVALUES, LAST_NAME, LN, FIRST_NAME, FN) ON TABLE SET PAGE NOPAGE END
The output is: