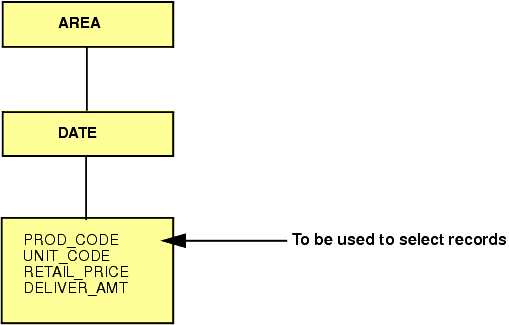
|
How to: |
|
Reference: |
If you are using certain network or hierarchical data sources such as IMS, CA-IDMS/DB, or FOCUS, you can rotate the data source, creating an alternate view which changes some of the segment relationships and enables you to access the segments in a different order. By reporting from an alternate view, you can do the following:
- Change the access path. For example, you can access data in a lower segment more quickly by promoting that segment to a higher level.
- Change the path structure of a data source. This option is especially helpful if you wish to create a report using several sort fields that are on different paths in the file. By changing the view of the file hierarchy, all the desired sort fields can be on the same path.
It should be noted that retrieval is controlled by the minimum referenced subtree. For more information, see Understanding the Efficiency of the Minimum Referenced Subtree in the Describing a Group of Fields chapter in the Describing Data manual.
For example, consider the regular and alternate views below:
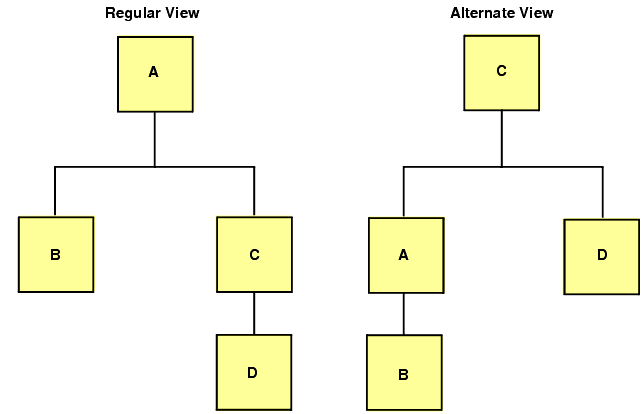
Since C is the root segment in the alternate view, particular instances of C can be selected faster.