Creation Rules for Data Files
|
How to: |
For a newly created data file, the location is determined as follows:
- An application set by APP HOLDDATA applies to all HOLD files.
- For FILEDEF command, one for each data file.
- For z/OS, native operating system allocations when supported.
The request that caused the file to be created determines the file DCB parameters, such as record length, record format, and so on.
For related information, see Output Redirection Commands.
Example: Sample Allocations by JCL
The following table contains sample allocations by JCL.
|
VSAM |
//VSAM01 DD DISP=SHR, DSN=qualif.DATA.VSAM This type of allocation requires the szero = y parameter in the edaserve.cfg file to support sharing of BufferPool Zero. |
|
Fixed |
//FIX01 DD DISP=SHR,DSN=qualif.FIXED.DATA |
|
PDS |
//MASTER DD DISP=SHR,DSN=qualif.MASTER.DATA |
|
FOCUS |
//CAR DD DISP=SHR,DSN=qualif.CAR.FOCUS |
Example: Sample DYNAM Commands
The following table contains samples of the DYNAM command.
|
VSAM |
DYNAM ALLOC FILE QVASM DA qualif.QVSAM.VSAM SHR REUSE |
|
Fixed |
DYNAM ALLOC FILE FILE1 DA qualif.FILE1.DATA SHR REUSE |
|
PDS |
DYNAM ALLOC FILE MASTER DA qualif.MASTER.DATA SHR REUSE |
|
FOCUS |
DYNAM ALLOC FILE CAR DA qualif.CAR.FOCUS SHR REUSE |
Syntax: How to Issue a FILEDEF Command
FI filedes DISK app/[appa.../]physfile.ftm
where:
- filedes
-
Is a file designation.
- app/[appa.../]
-
Is an application name. It can be a nested application name.
- physfile.ftm
-
Is a physical file located in the application.
Syntax: How to Issue a FILEDEF Command to Concatenate Files
FI[LEDEF] concatname DISK [app1/]filename1.ext FI[LEDEF] name2 DISK [app2/]filename2.ext ... FI[LEDEF] namen DISK [appn/]filenamen.ext FI[LEDEF] concatname CONCAT name2 ... namen
where:
- concatname
-
Is the ddname for one of the files and the name for the concatenated files. Use this name in a request. The individual ddnames will not be available once they are used in a FILEDEF CONCAT command.
- name2 ... namen
-
Are ddnames for the files that will be added to the concatenation.
- app1 ... appn
-
Are application names. They can be nested application names.
- filename1.ext ...filenamen.ext
-
Are the physical file names.
Example: Concatenating Files Using FILEDEF
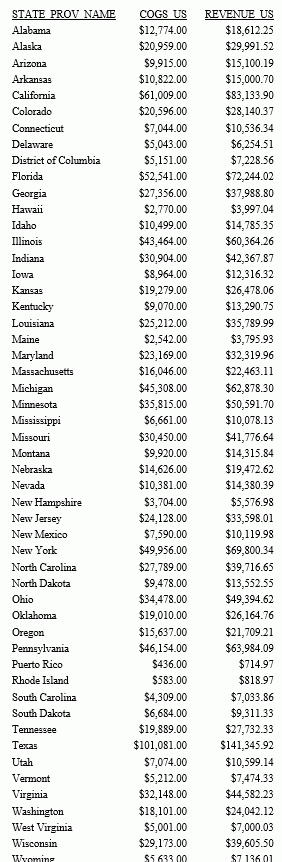
The following request creates three files, file1.ftm, file2.ftm, and file3.ftm.
APP HOLD app1 TABLE FILE WF_RETAIL_LITE SUM COGS_US REVENUE_US BY STATE_PROV_NAME WHERE STATE_PROV_NAME LE 'F' WHERE COUNTRY_NAME EQ 'United States' ON TABLE HOLD AS file1 FORMAT ALPHA END -RUN TABLE FILE WF_RETAIL_LITE SUM COGS_US REVENUE_US BY STATE_PROV_NAME WHERE STATE_PROV_NAME GT 'F' AND STATE_PROV_NAME LE 'M' WHERE COUNTRY_NAME EQ 'United States' ON TABLE HOLD AS file2 FORMAT ALPHA END -RUN TABLE FILE WF_RETAIL_LITE SUM COGS_US REVENUE_US BY STATE_PROV_NAME WHERE STATE_PROV_NAME GT 'M' WHERE COUNTRY_NAME EQ 'United States' ON TABLE HOLD AS file3 FORMAT ALPHA END
The following commands concatenate the three files.
FILEDEF FILE1 DISK app1/file1.ftm FILEDEF FILE2 DISK app1/file2.ftm FILEDEF FILE3 DISK app1/file3.ftm FILEDEF FILE1 CONCAT FILE2 FILE3
The following procedure issues a request against the concatenated files.
TABLE FILE FILE1 SUM COGS_US REVENUE_US BY STATE_PROV_NAME ON TABLE SET PAGE NOPAGE ON TABLE SET STYLE * GRID=OFF, SIZE=8,$ END
The output is shown in the following image.
Syntax: How to Issue a FILEDEF Command for a Native MVS Data Set
FI filedes DISK "//'NATIVE.MVS.DATASET'"
where:
- filedes
-
Is a file designation.
- NATIVE.MVS.DATASET
-
Is a Native MVS data set. It can contain any number of qualifiers, up to 44 characters long.
Syntax: How to Issue a USE command
The USE command can be issued instead of an allocation command for FOCUS data sources. The USE command is the only mechanism for accessing files on the sink machine.
Example: Sample USE Commands
The USE command supports renaming of Master Files and concatenation of data sets. The USE command is the only mechanism for accessing files on the sink machine.
Renaming a Master File
USE CAR1 AS CAR END
Concatenating Master Files
USE CAR1 AS CAR CAR2 AS CAR END
Accessing Files on a Sink Machine
USE CAR1 ON FOCSU01 END